Physical Exercise is necessary for anybody looking to take care of their health. Physical activity reduces your risk of a heart attack by improving your cardiovascular health, helps manage stress, and helps you manage your weight.
Physical exercise is categorized into two main categories – aerobic and anaerobic. This classification is done based on the energy source used by the muscles to contract.
Aerobic Exercise vs Anaerobic Exercise
The main difference between Aerobic exercise and Anaerobic exercise is that Aerobic exercises depend on the inhalation of oxygen by the body as a source of energy. Whereas for anaerobic exercise, the muscles depend on other alternate energy sources.

Aerobic exercise is dependent on oxygen intake as an energy source. This exercise incorporates larger muscle groups for longer durations, is more steady, and the muscles rely on aerobic metabolism to function.
Anaerobic exercise does not depend on oxygen intake for energy. This type of exercise is a highly intense physical activity for a short duration. The muscles do not directly depend on the oxygen breathed in for energy.
Comparison Table between Aerobic exercise and Anaerobic exercise
| Parameters of Comparison | Aerobic Exercise | Anaerobic Exercise |
| Dependence on oxygen intake | Aerobic exercises are highly dependent on the intake of oxygen as an energy source. to extract ATPs from amino acids, fatty acids and carbohydrates. | Anaerobic exercises do not depend on inhaled oxygen as a source of energy. |
| Intensity of exercise | Aerobic exercises are less intense in nature in comparison to anaerobic exercises. | Anaerobic exercises are very intense on the targeted muscle groups. |
| Duration of exercise. | Aerobic exercises consist of a longer exercise duration between breaks. | Anaerobic exercises rapidly switch between exercises and break intervals to increase intensity. |
| Production of ATPs | Production of ATPs is significantly higher as muscles depend on Adenosine Triphosphates for energy. | Production of ATPs is very less as muscles are not dependent on Adenosine Triphosphates for energy. |
| Muscle Groups Incorporated | Aerobic Exercise incorporates larger muscle groups for a longer and more rhythmic duration | Anaerobic exercise targets very specific muscles/muscle groups during exercise. |
What is Aerobic Exercise?
Aerobic exercises are a type of exercise that focuses on incorporating larger muscle groups. The exercises are highly rhythmic in nature. They are comparatively less intense, and the exercises last for longer intervals.
Aerobic exercise is a type of exercise that is highly dependent on oxygen intake to supply muscles with energy. The oxygen extracts ATPs from amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates.
Certain examples of Aerobic exercises include cycling, hiking, dancing, jogging, running, swimming, and even walking.
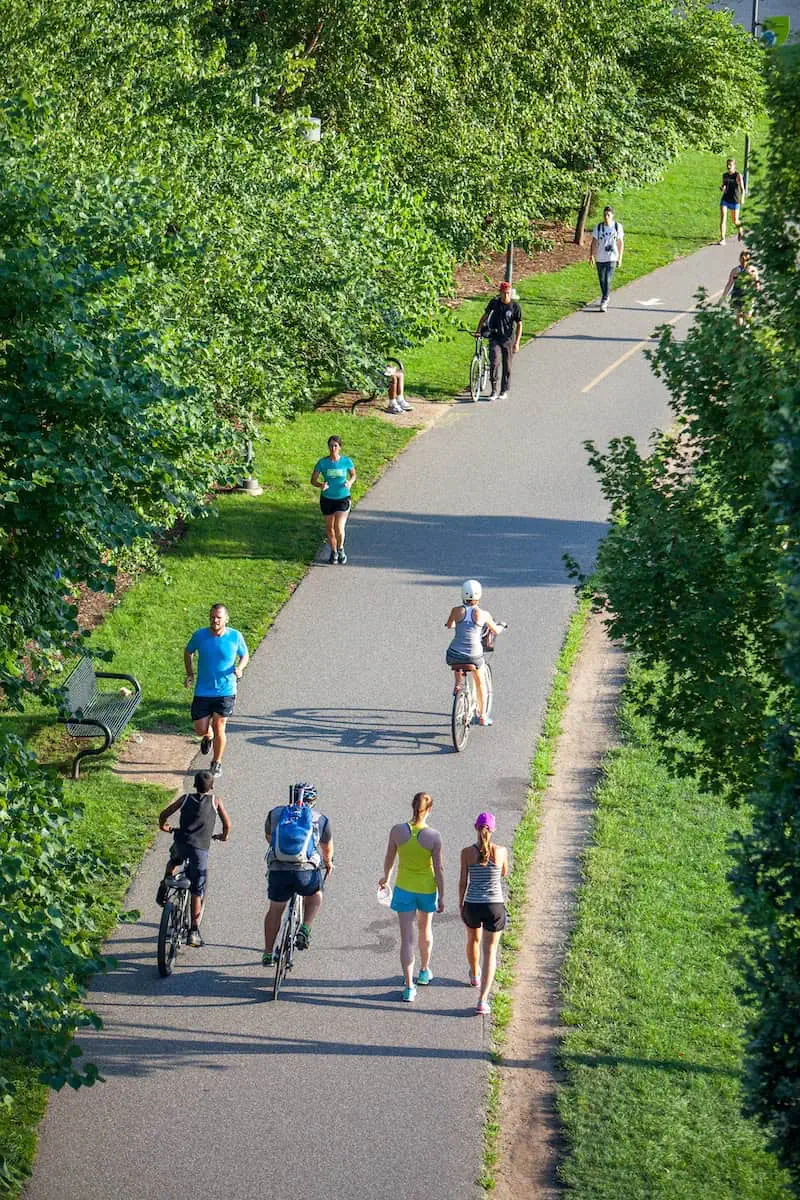
Aerobic exercise has shown humongous benefits in increasing Cardiovascular health. It has also shown a small yet significant decrease in total cholesterol.
However, the effect of aerobic exercise is limited to the frequency and quantity of the exercise. Studies show that 1 to 2.5 hours of aerobic exercise over 2-3 times a week is optimal.
Exercise frequency higher than that has shown no significant change in mortality risk.
What is Anaerobic Exercise?
Anaerobic exercise is a type of exercise that targets a very specific muscle or a set of specific muscles. It is an intense physical activity that lasts for a very short duration.
Anaerobic exercises depend on energy sources within the contracting muscles. They do not use inhaled oxygen as an energy source.
This process, in particular, produces a lesser amount of ATPs in comparison to aerobic exercise. Instead, it results in the production of high amounts of lactic acid.
Some anaerobic exercises include sprinting, HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training), power-lifting, etc.
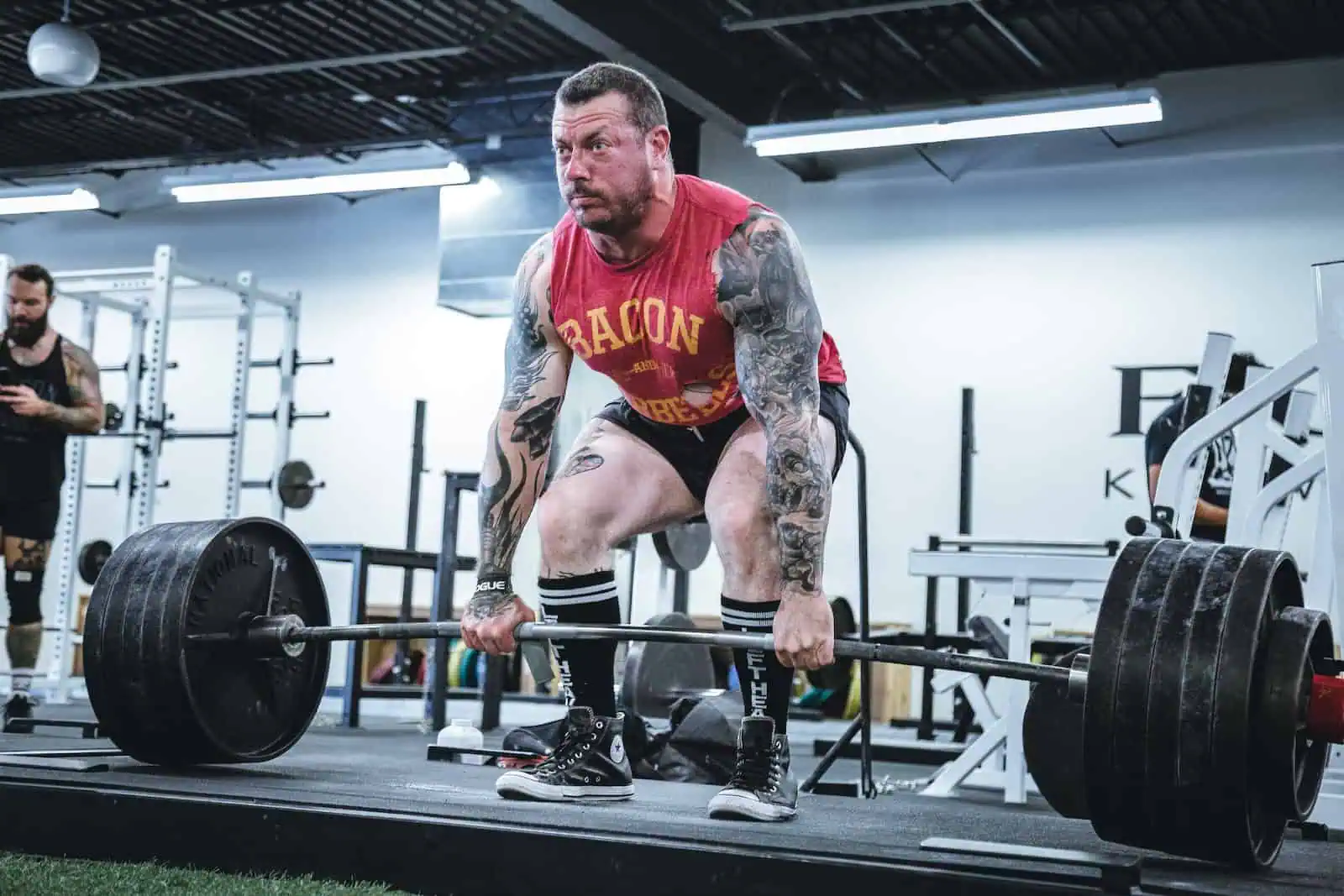

Similar to its counterpart, anaerobic exercise also greatly benefits your cardiovascular health.
Anaerobic exercises can be highly taxing on the body. It is recommended that an average individual perform anaerobic exercise about 2 to 3 times a week, with a day of rest in between.
However, some recent speculation about this form of exercise has also come to light.
An Iranian study concluded that anaerobic exercise may lead to lesser Human Growth Hormone (HGH) production.
Main Differences Between Aerobic Exercise and Anaerobic Exercise
- Aerobic exercises are those types of exercises that are highly dependent on inhaled oxygen as an energy source for the muscles to contract. Anaerobic exercises, being the opposite, are not very dependent on the oxygen intake to be used as an energy source.
- Aerobic Exercises focus on larger muscle groups, whereas Anaerobic exercises target specific muscle groups.
- Aerobic exercises last longer while focusing on the larger muscle groups. Anaerobic exercises last for a very short duration in comparison.
- Anaerobic exercises are highly intense on the targeted muscle groups and, thus, can only be maintained for a shorter duration. On the other hand, aerobic exercises are less intense and, thus, can be maintained for much longer.
- Aerobic exercise produces many ATPs extracted from amino acids, carbohydrates, and fatty acids. As anaerobic exercises are not dependent on inhaled oxygen, they produce a significantly lesser amount of ATPs and a high amount of lactic acid.
Conclusion
Both these types of exercises are beneficial to your cardiovascular health and overall physical health. Along with improving your physical health, they are also great reducers of stress and anxiety and are a must in today’s highly sedentary lifestyle.
Each type has its own pros and cons. Therefore, these exercises should be balanced for optimum benefits, preferably after a consultation with a medically trained professional.