Exact Answer: 24 hours
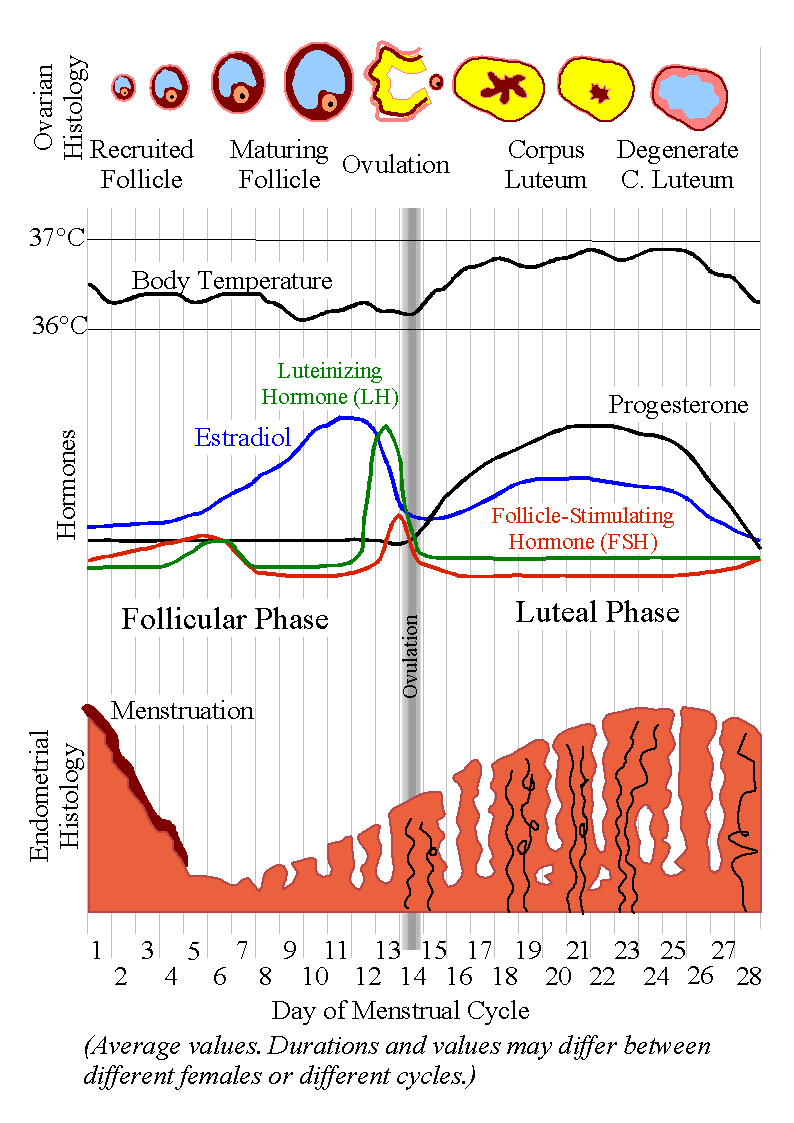
Basal body temperature (BBT) is a person’s temperature when a woman is at rest. Women need to track their BBT so they know when they are ovulating, with this a woman can determine when she is most and least likely to become pregnant.
The eggs are normally fertile within about 12-24 hours after ovulation. If you avoid sex for a few days after ovulation it can help prevent pregnancy. One should be aware that the cycle may change making it difficult to determine ovulation.

How Long After Ovulation Does BBT Rise?
The basal body temperature (BBT) will drop slightly before ovulation begins, that is 24 hours after the release of the egg, its temperature rises and is maintained for several days. Before ovulation, women’s average body temperature is 97 ° F and 97.5 ° F. After ovulation, it rises to 97.6 ° F at 98.6° F.
You can track your cycle by taking BBT every morning using a body temperature calculator or thermometer. Check your temperature at the same time every day before getting out of bed. Then, take notes of the results. If you have a somewhat regular cycle, the chart can help you predict when you will ovulate next.
Tracking the BBT more can make your predictions more accurate. Often taking BBT helps to measure and keep a track of ovulation; however, BBT alone cannot predict future ovulation.
BBT is slightly lower during the follicular phase which is also known as the first half of the menstrual cycle, increases after ovulation, and remains elevated during the luteal phase that is the second half of the menstrual cycle.
The change in temperature after ovulation is negligible in which the BBT only increases 0.5 ° F / 0.3 ° C to 1.0 ° F / 0.6 ° C and can easily be affected by factors such as illness, alcohol, and changes in sleep, this change occurs in response to the amount of progesterone released after ovulation.
Summary:
| Body Temperature | Time (in days) |
| 97.9 F | 2 |
| 97.2 | 14 |
| 98.1 | 25 |
| 97.5 | 27 |
Why Does It Take So Long For BBT To Rise After Ovulation?
The change in Basal body temperature (BBT) depends on a number of factors, including hormone levels. During ovulation, the hormone progesterone causes a rise in temperature. It rises higher within two weeks of waiting. Then, just before your period begins, your progesterone hormone levels drop.
This means that your basal body temperature will also drop if you are not pregnant, in which case your temperature will continue to rise due to high progesterone levels.
When you observe the Basal body temperature charts, you are basically looking for the big picture, not the temperature rise in one place or another. Your temperature may rise and fall as your cycle continues, but you should notice a biphasic pattern after ovulation which means that the average temperature is lower before ovulation than after ovulation.
By observing at least three consecutive increases in average temperature, you will most likely know that ovulation occurred the day before the first comes out to be maximum.

A basal body temperature chart is a great way to keep track of your cycles and ovulation patterns, and can also help your doctor determine if ovulatory infertility is possible. If you are concerned that you are not ovulating, bring your BBT card to your gynecologist that is because when pregnancy is detected, the BBT chart can give only small clues.
Conclusion
In cases related to BBT and Ovulation, it may take some time to get used to monitoring and recording temperature and learning about changes in your body as well as the other signs that you are in a cycle include breast tenderness, pain around the ovaries, and a condition of the cervical lining.
So, many women keep track of this when they start and when they end. However, you can always consult a doctor for further queries. No matter how tempting it can be to look for early signs of pregnancy and although can be stressful to wait for a pregnancy test at the same time.