Exact Answer: After 4 to 10 weeks
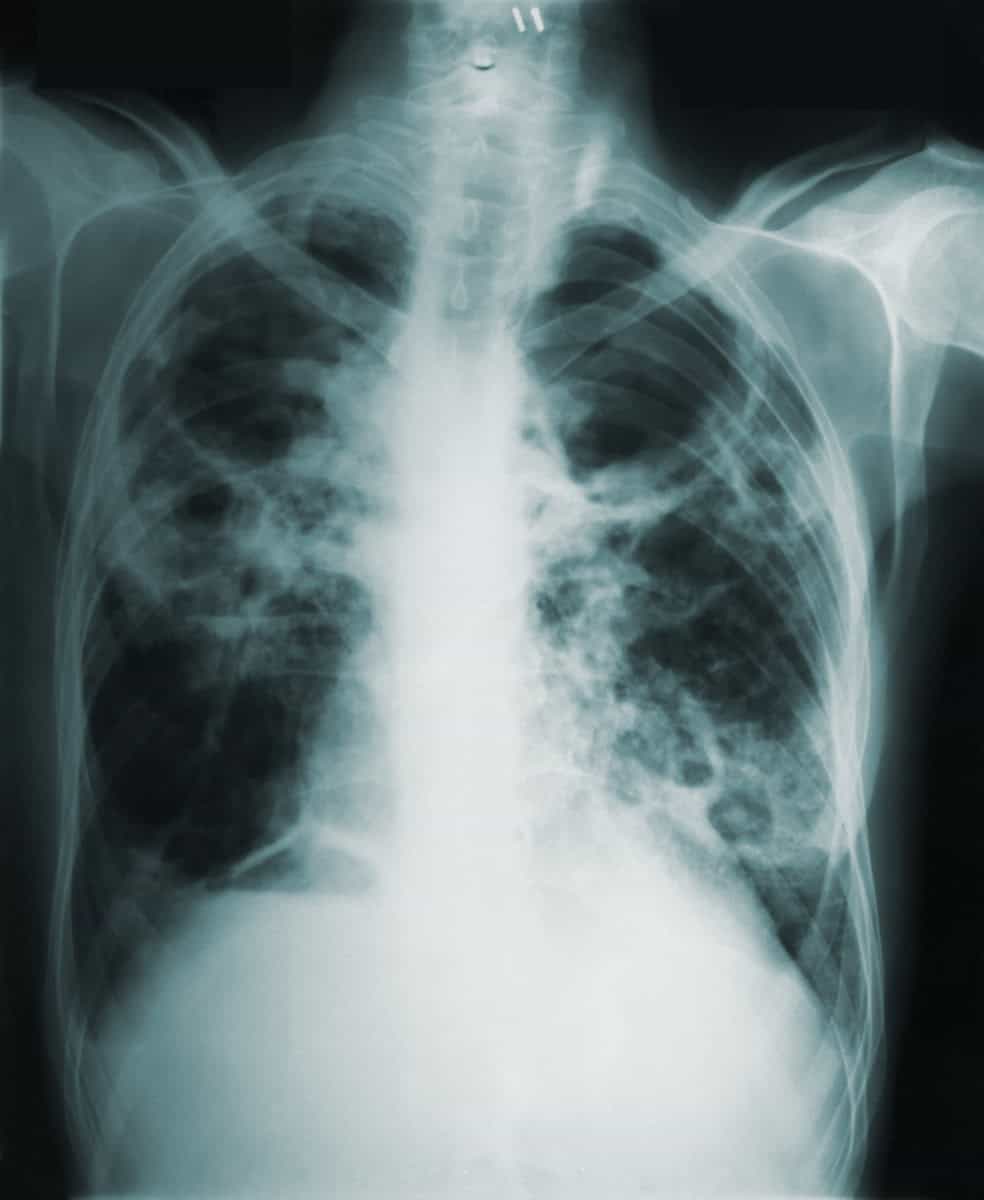
An infectious disease that shares its tentacles from person to person easily is tuberculosis. It is one of those diseases, which mainly starts affecting the lungs from the initial stage. The symptoms of the disease can be detected when someone starts coughing. Sometimes, the cough may also include blood tings, along with weight loss, mild fever, and insomniac sweats at night.
However, one can treat it with the assistance of medical professionals and requires some specialized medical treatment. But alongside the exposure, one should keep in mind that it spreads from person to person. Hence, when the patient sneezes, sings, speaks, or coughs. And, this exposure is tested within 4 to 10 weeks. The person then has chances of spreading.

How Long After TB Exposure Should You Be Tested?
| Time Within Which The Exposure Happens | 2-3 weeks |
| The Germ Stays Within The Body | 10 weeks – 2 years |
Tuberculosis, also known as TB, can also be prevented by taking the vaccine. But the prevention of this disease after taking the vaccine is only 80 percent. After taking the vaccine, if an uninfected person starts talking and conversing with the infected person, there is a severe chance of getting infected. As it is the lungs that mainly get affected by tuberculosis, it all spreads by the air.
The coughing, sneezing, singing, and talking directly to the patient make it spread the bacteria through the air. Tuberculosis is due to the bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It starts affecting the lungs from the initial stage. But apart from the lungs, the other body parts include the spine, brain, or kidney. But not to be worried, as the disease is curable and preventable with the necessary precautionary measures.
But the person who is not infected with the germ and is neither vaccinated bears a higher chance of getting TB exposure from the infected one. The exposure starts with having mild pain in the chest. It comes along with coughing blood, which can make the person feel bad. Once the symptoms start rising, the person should be consulted to the doctor and precautionary measures should start taking place.
The medication contains at least two weeks before acting enough. The contagious symptom of the disease remains for these two weeks while taking the medicine. After the medication, the treatment may continue. But, the contagious nature fades away. Hence precautionary measures are a must. And, one should not worry much.
Why Should You Be Tested So Long After TB Exposure?
Although with the starting of the medication, the germs of the disease start decreasing, the spreading may continue. It is because the germs double up within the body. Also, the newly developed versions of the infecting agent contain the power to spread. Hence this period of two weeks becomes too important to remain concerned and not let the germ spread its tentacles.
With a lot of research and studies, the incubation period of tuberculosis remains from a few months to a couple of years. The activation period of these eggs remains so long. Due to this, the treatment carries on for this long period. Due to this reason, the TB exposure can get tested active for 4 to 10 weeks. But after a maximum of 2 to 3 weeks, the germ loses the power of spreading and no longer is a danger for the not affected patients.
The infections of tuberculosis are of three stages. Exposure is the first stage of the infection. The latent stage comes as the second one. The third stage is the active disease. The disease can be diagnosed either by a TB skin test or a typical blood test. But every time, it is better to do the other testing also to get a better preview.
But whatever the stage of the TB, the treatment should be carried out extensively. If left untreated for a long period or not fully treated within the initial time, the disease can cause life-threatening concerns. Hence, these are the reasons why it takes so long after the exposure to get tested.
Conclusion
Once the tuberculosis germ gets passed into the body by breath, it can naturally become inactive after the treatment. But the germs remain alive within the body for a long period and may also rise and become active later on. However, the chances of this are low. Still, the treatment needs to be too effective to avoid this.
However, the period during which the germ can spread a lot to the not-infected person should be a major concern. After two weeks, the patient may test positive for 4 to 10 weeks. It is because the germ is still present within the body, but it is no longer contagious.